A dictionary of Greek and Roman antiquities.. . stridens i?i limine cardo, Virg. Ciris, 222; Eurip.Phoen. 114—116, Schol. ad loc.). The Greeks and Romans also used hinges ex-actly like those now in common use. Four Romanhinges of bronze, preserved in the British Museum,are here shown.. The form of the door above delineated makes itmanifest why the principal line laid down in sur-veying land was called * cardo (Festus, s. v. De-cumanus ; Isid. Orig. xv. 14) ; and it further ex-plains the application of the same term to theNorth Pole, the supposed pivot on which theheavens revolved. (Varr. De Re
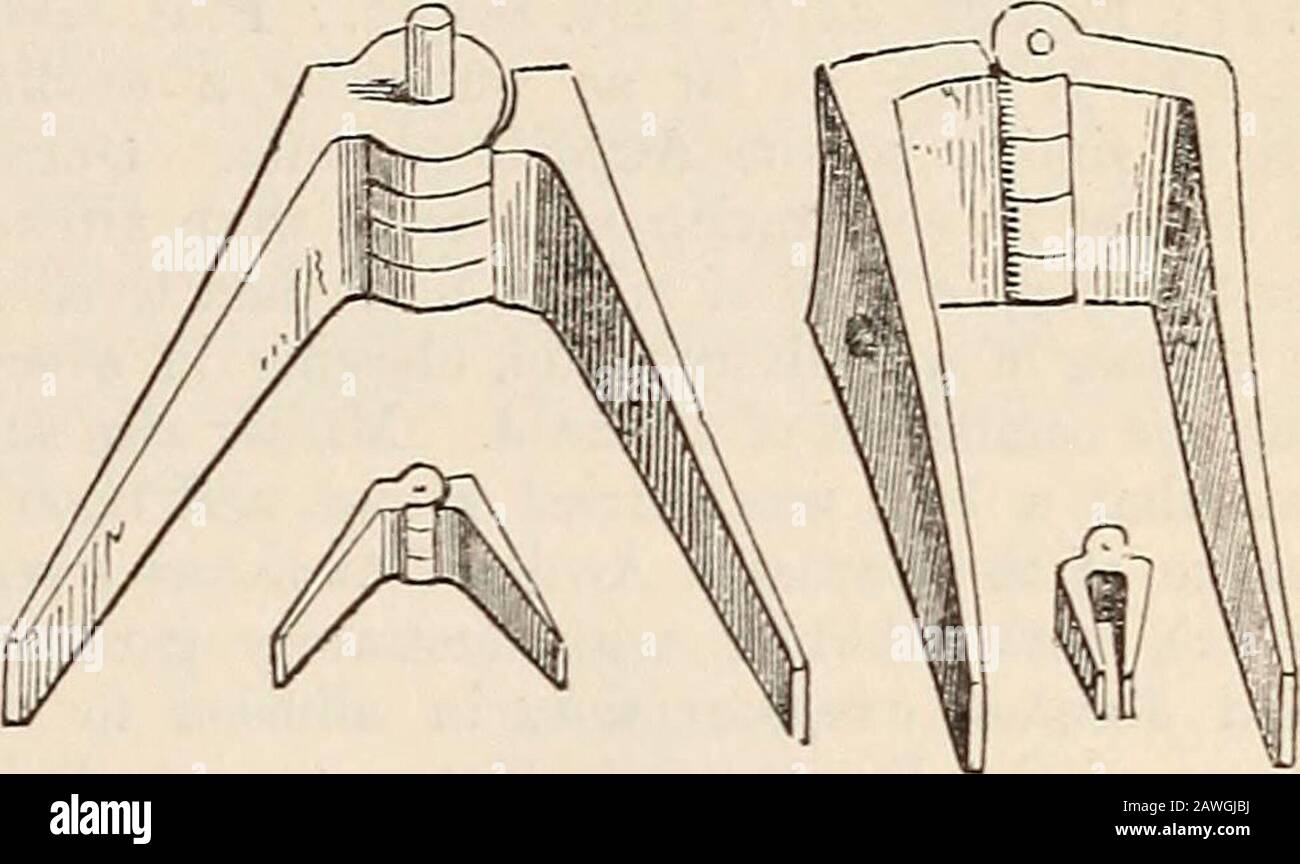
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AWGJBJFile size:
7.1 MB (217.2 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
2048 x 1220 px | 34.7 x 20.7 cm | 13.7 x 8.1 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
A dictionary of Greek and Roman antiquities.. . stridens i?i limine cardo, Virg. Ciris, 222; Eurip.Phoen. 114—116, Schol. ad loc.). The Greeks and Romans also used hinges ex-actly like those now in common use. Four Romanhinges of bronze, preserved in the British Museum, are here shown.. The form of the door above delineated makes itmanifest why the principal line laid down in sur-veying land was called * cardo (Festus, s. v. De-cumanus ; Isid. Orig. xv. 14) ; and it further ex-plains the application of the same term to theNorth Pole, the supposed pivot on which theheavens revolved. (Varr. De Re Rust. i. 2 ; Ovid, Ex Ponto, ii. 10. 45.) The lower extremity ofthe universe was conceived to turn upon anotherpivot, corresponding to that at the bottom of thedoor (Cic. De Nat. Deor. ii. 41; Vitruv. vi. 1, ix. 1) ; and the conception of these two principalpoints in geography and astronomy led to the ap-plication of the same term to the East and Westalso. (Lucan. v. 71.) Hence our four points ofthe compass are called by ancient writers quatuorcardines orbis terrarum, and the four principalwinds, N. S. E. and W., are the cardinales ventL(Serv. ad Aen. i. 85.) [J. Y.J CARINA. [Navis.] CARMENTALIA, an old Roman festival ce-lebrated in honour of the nymph Carmenta orCarmentis, for