. Diseases of plants induced by cryptogamic parasites : introduction to the study of pathogenic Fungi, slime-Fungi, bacteria, & Algae . Plant diseases; Parasitic plants; Fungi. 312 USTILAGINEAE. germination produce a thread-like promyeelium bearing apical conidia, which conjugate in pairs before emerging from the host-tissues. The following species form conidia on the host-plant: Entyloma serotinum Schroet. occurs on leaves of Symphytum tuberosum, S. officincdis, and Borago officinalis. E. canescens Schroet. On Myosotis (Britain). E. fuscum Schroet. On Papaver Rhoeas and /'. Argemone. E. b
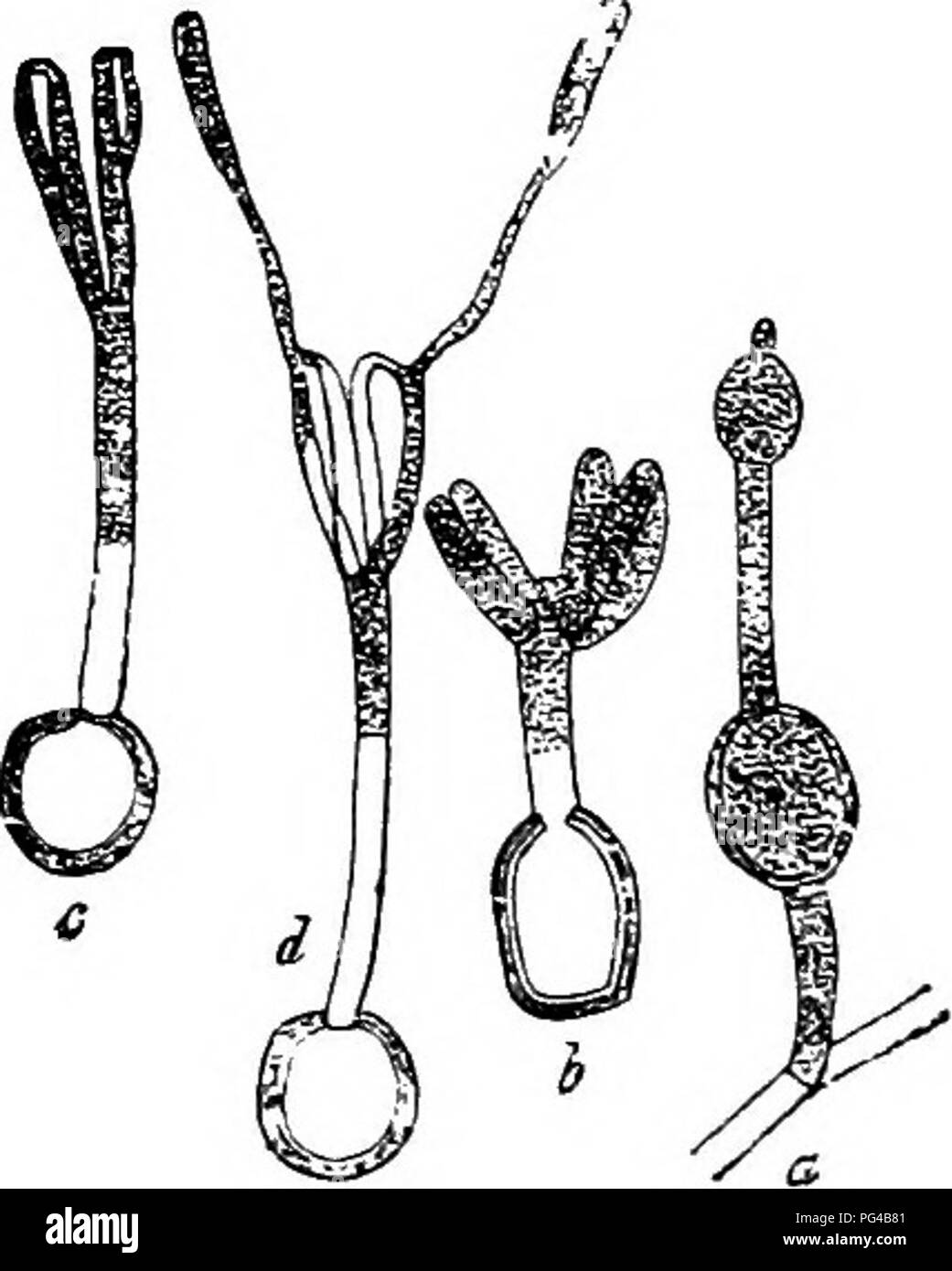
Image details
Contributor:
Central Historic Books / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
PG4B81File size:
7.1 MB (199.4 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1415 x 1766 px | 24 x 29.9 cm | 9.4 x 11.8 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Diseases of plants induced by cryptogamic parasites : introduction to the study of pathogenic Fungi, slime-Fungi, bacteria, & Algae . Plant diseases; Parasitic plants; Fungi. 312 USTILAGINEAE. germination produce a thread-like promyeelium bearing apical conidia, which conjugate in pairs before emerging from the host-tissues. The following species form conidia on the host-plant: Entyloma serotinum Schroet. occurs on leaves of Symphytum tuberosum, S. officincdis, and Borago officinalis. E. canescens Schroet. On Myosotis (Britain). E. fuscum Schroet. On Papaver Rhoeas and /'. Argemone. E. bicolor Zopf. On Papaver Rhoeas and P. dubium (Britain). E. ranunculi (Bon.) forms white spots on species of Ranunculus. Tufts of hyphae emerge from the stomata and form conidia, which on germination again give o£F conidia.' (Britain.) E. corydalis De Bary on Corydalis cava and C. solida. E. helosdadii Magn. on Heloscladium nodiflorum. These do not produce conidia on the host-plant: E. thalictri Schroet. on ThaUctrum minus (U.S. America). E. vemiculosum Pass, on Ranuncuhis lanuginosus. E. Fischeri Thtim. on Stenactis bellidi- Aora. E. chrysosplenii (Berk, et Br.) on Ch-ysosplenium altemifolium (Britain). E. linariae Schroet. on Linaria vulgaris (TT.S. America). E. picridis Eostr. on Picris hieracoides. E. eryngii (Corda) on EryTigium, planum and E. campestre. Calendula, Hieracium, Amoseris, Arnica, . Fig. 16S.—Entyloma calendulae. a, My- celial filament, with two young resting- spores. by Resting-spore germinating; the anterior pair of primary conidia shows conjugation or fusion at the base. Entyloma microsporv.m. c, Germinat- ing resting-spore; four primary conidia fusing in pairs at their apices, d. The same specimen seTen hours later; com- mencement of abjunction of a secondary sporidium on each pair. (After De Bary.) E. calendulae (Oudem.) on Bellidiastrum, etc. (Britain) (Fig. 168). E. crastophilum Sacc. on Poa and Dactylis in Italy. The following produce gall-like swelli