Phagocytosis of Yeast Particle, Streptococcus pyogenes, SEM
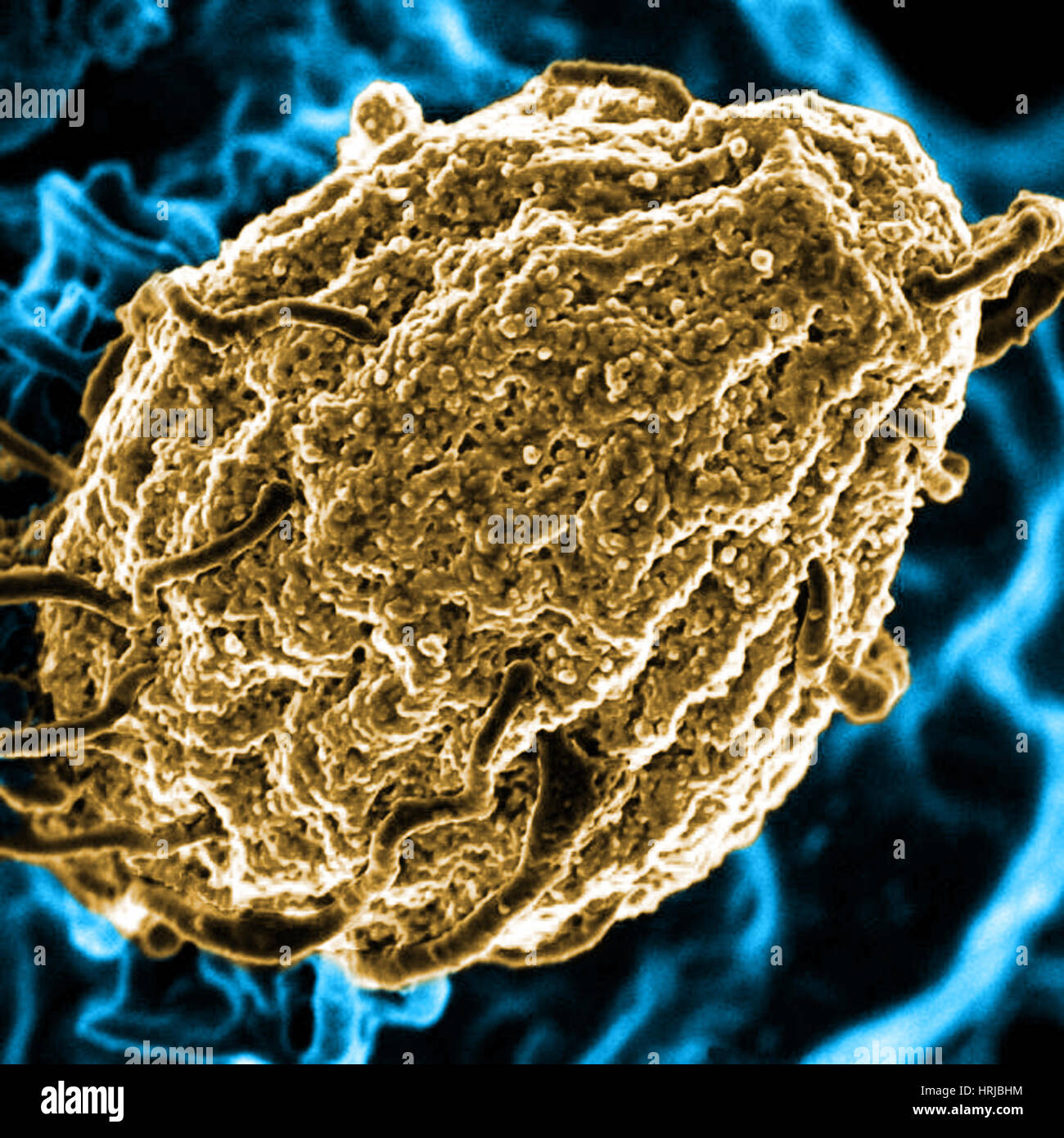
Image details
Contributor:
Science History Images / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
HRJBHMFile size:
28.4 MB (1.3 MB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
3150 x 3150 px | 26.7 x 26.7 cm | 10.5 x 10.5 inches | 300dpiPhotographer:
Photo ResearchersMore information:
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Scanning electron micrograph of phagocytosis of yeast particle, Streptococcus pyogenese. Phagocytosis is the engulfing and ingestion of bacteria or other foreign bodies by phagocytes. Streptococcus pyogenese is a spherical gram-positive bacterium that grows in long chains and is the cause of Group A streptococcal infections. Streptococcus pyogenes is a spherical, Gram-positive bacterium that is the cause of group A streptococcal infections. Streptococcus pyogenes displays streptococcal group A antigen on its cell wall. Streptococcus pyogenes typically produces large zones of beta-hemolysis (the complete disruption of erythrocytes and the release of hemoglobin) when cultured on blood agar plates, and are therefore also called Group A (beta-hemolytic) Streptococcus (abbreviated GABHS). Streptococci are catalase-negative. In ideal conditions, S. pyogenes has an incubation period of approximately 1-3 days. It is an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin flora. It is estimated that there are more than 700 million infections world wide each year and over 650, 000 cases of severe, invasive infections that have a mortality rate of 25 %.