. The anatomy of the domestic animals . Veterinary anatomy. BONES OF THE PELVIC LIMB 153 Chanter major. The third trochanter is absent. The supracondyloid fossa is shallow. The proximal extremity is very wide. The head is smaller than in the horse, and the articular surface extends considerably on the upper surface of the necK ifie fovea capitis is a small depression on the middle of the head for the attachment of the round ligament. The neck is well defined except above The trochanter major is very massive and is undivided; its lateral surface is very rough. Fig. 155.—Right Femur of Ox; Poste
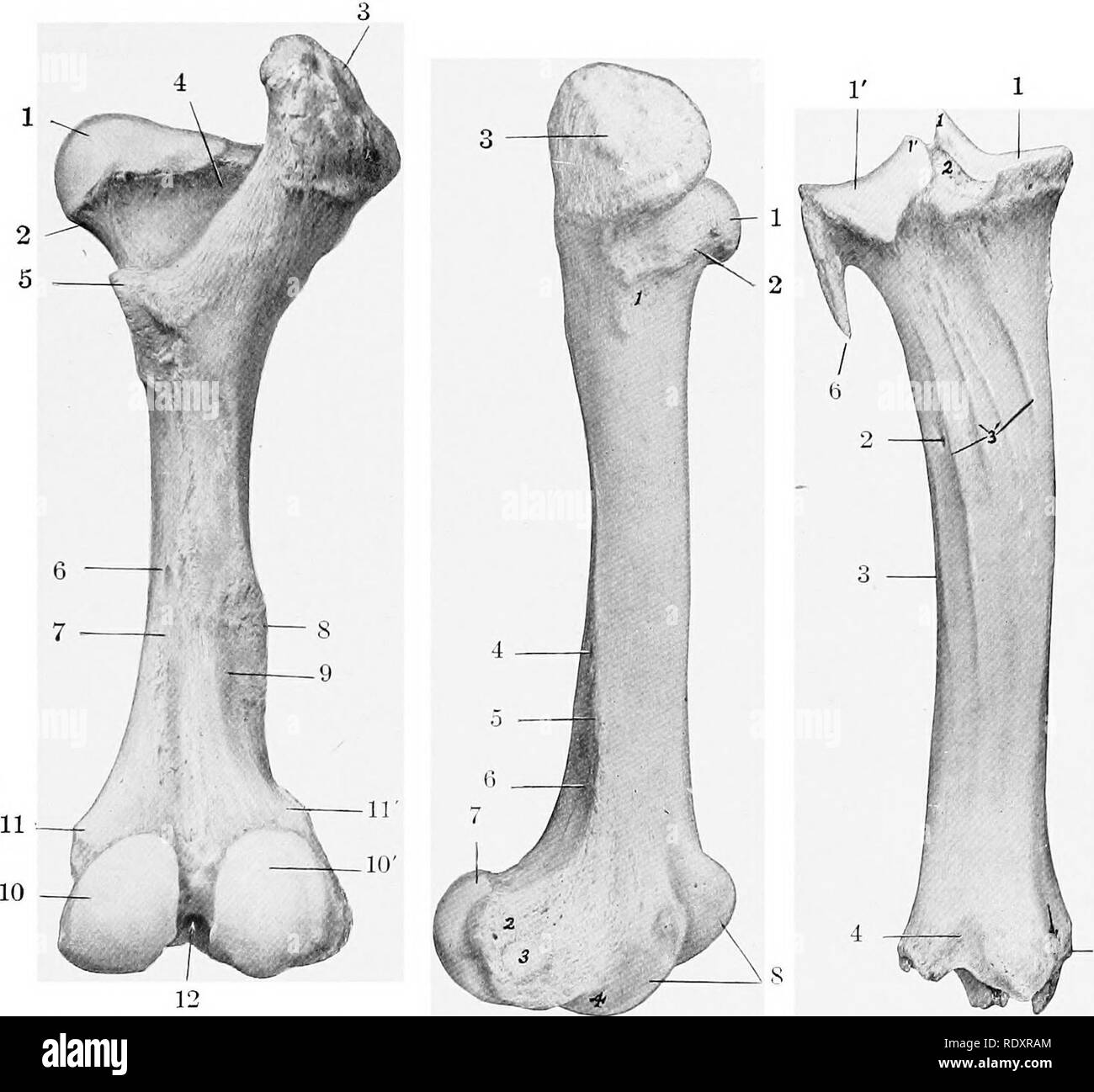
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDXRAMFile size:
7.2 MB (256.8 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1640 x 1524 px | 27.8 x 25.8 cm | 10.9 x 10.2 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. The anatomy of the domestic animals . Veterinary anatomy. BONES OF THE PELVIC LIMB 153 Chanter major. The third trochanter is absent. The supracondyloid fossa is shallow. The proximal extremity is very wide. The head is smaller than in the horse, and the articular surface extends considerably on the upper surface of the necK ifie fovea capitis is a small depression on the middle of the head for the attachment of the round ligament. The neck is well defined except above The trochanter major is very massive and is undivided; its lateral surface is very rough. Fig. 155.—Right Femur of Ox; Poste- rior View. 1, Head; 2, neck; 3, trochanter ma- jor; 4, trochanteric fossa; 5, trochanter minor; 6, nutrient foramen; 7, vascular groove; S, lateral supracondyloid crest; 9, supracondyloid fossa; 10, 10', medial and, lateral condyles; 11, 11', medial and lateral epicondj'les; 12, intercondyloid Fig. 156.—Right Femur of Ox; Lateral View. Numbers around bone: 1, Head; 2, neck; 3, trochanter major; 4, lateral border; 5, lateral supracondyloid crest; 6, supra- condyloid fossa; 7, lateral condyle; 8, trochlea. Numbers on bone: 1, Eminence for attachment of gluteus profundus; 2, lateral epicondyle; 3, depression for origin of popliteus muscle; 4, extensor fossa. Fig. 157.—Left Tibia .vxd Prox- imal Part of Fibula of Ox; Posterior View. Numbers around bones: 1, 1', Medial and lateral condyles of tibia; 2, nutrient foramen; 3, lateral border; 4, distal extrem- ity; 5, medial malleolus; 6, shaft of fibula. Numbers on bone: 1, 1', Tubercles of spine; 2, intercondy- loid fossa; 3, muscular lines. Arrow indicates groove for flexor digitalis longus. The trochanteric fossa is deep, but does not extend so far distally as in the horse. The distal end presents no very striking differential features, but the ridges of the trochlea are less oblique than in the horse, and converge very slightly below. The proximal extremity unites with the shaft at about three and one-half years, the distal